Sat, Dec 20, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 27, Issue 2 (2017)
IJAUP 2017, 27(2) |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Rafieian M, Alizadeh A. An Integrated Approach of Spatial Justice and Structure to Detect Spatial Conflicts in Yazd City. IJAUP 2017; 27 (2)
URL: http://ijaup.iust.ac.ir/article-1-250-en.html
URL: http://ijaup.iust.ac.ir/article-1-250-en.html
1- Art and Architecture Faculty, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran, Art and Architecture Faculty, Tarbiat Modares University , rafiei_m@modares.ac.ir
2- Tehran, Iran., Tarbiat Modares University
2- Tehran, Iran., Tarbiat Modares University
Abstract:
According to several types of research, one of the most important issues and principles of sustainable development that urban professionals pay attention to it recently is Just City. One aspect of Justice in cities, spatial justice, has particular significance by Unequal and discordant Expanding in cities regarding creating unequal areas. On the other hand, the urban spatial structure affects the equal distribution of elements and services. If this structure is devoid of justice ideology will lead to a complex social crisis and spatial issues as spatial conflict. Accordingly, this study aims to analyse the spatial justice and structure in the case of Yazd city to know how they influence each other. Spatial justice is examined from the view of "Equality of opportunity". Involved criteria are "equality", "Physical diversity", "human diversity" and "urban spaces", and spatial structure based on “Space Syntax” technique with "integration", "control", "connect" and " intelligibility " parameters. These criteria are Scored and analysed by FDAHP techniques and GIS. The result shows favourable status in the Central District, and as getting away from the disadvantaged downtown District increased. On the other hand, the spatial structure analysis reveals the most spatial coherent analogue the north-south axis with a little depth and isolated District (Spatial segregations) have located in the corners and edges of the city. Results from the superposition of these two analysis layers show a compatibility relation between the spatial structure of Yazd and the pattern of justice distribution except in the central and historical centre.
Full-Text [PDF 1335 kb]
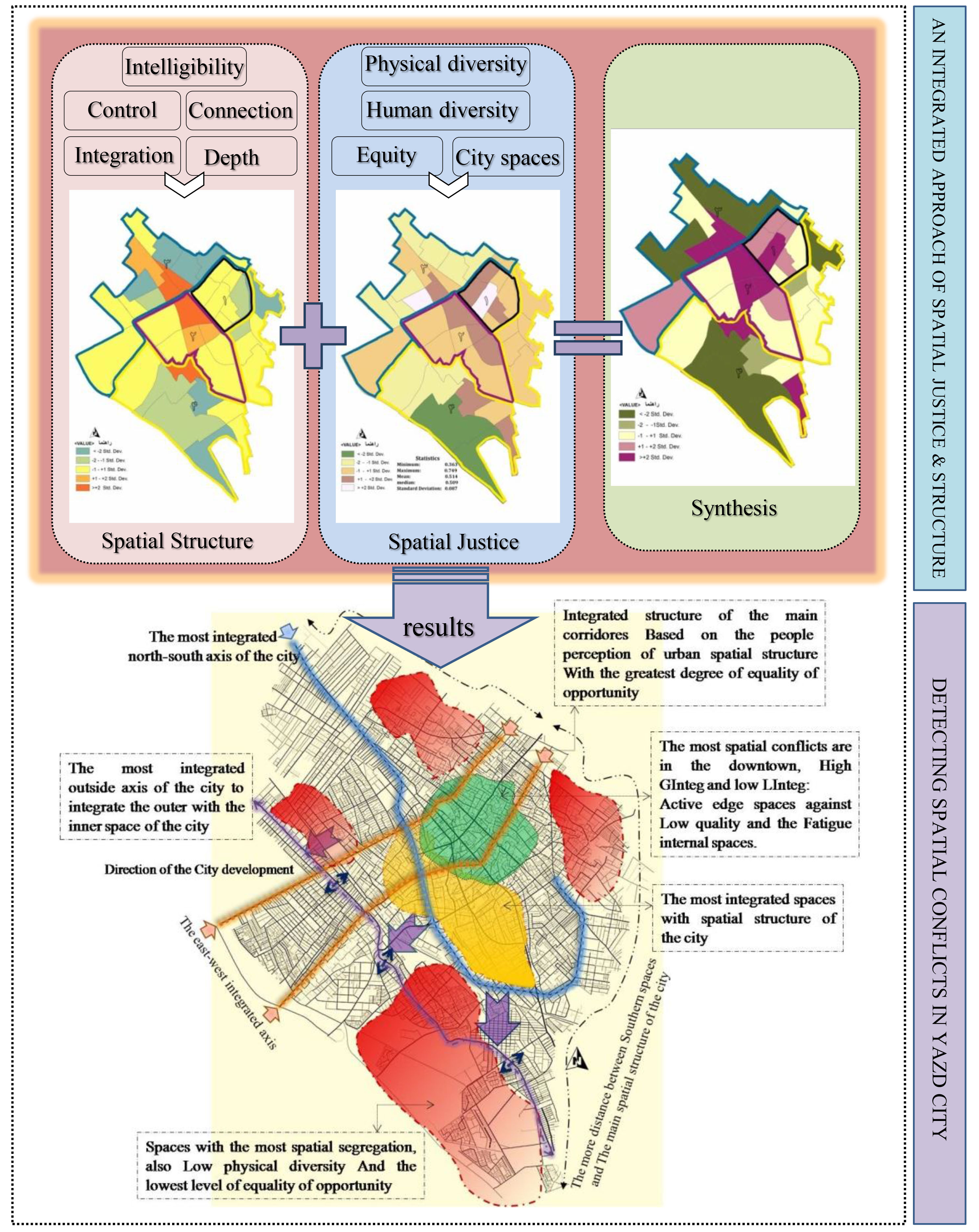

- Lack of desirable spatial quality at the central districts is due to incoherence and no integration structure with the entire city.
- The districts which have more coherent spatial structure have a better condition in justice distribution.
- Spatial structure is employed to argue that physical forms and spaces can alternately promote or suppress the sense of justice in the city.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Urban Planning
| Rights and permissions | |
 | This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |





