BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
URL: http://ijaup.iust.ac.ir/article-1-254-en.html
2- Master of Architecture, Shiraz University
3- 3Assisstant professor, Evin,Shahid Bheheshti ,
Daylight in classrooms is a critical factor in school design, in terms of its impact on students’ health, learning and visual performance. Providing adequate amount of evenly distributed daylight and glare prevention are important challenges in classroom design. Window configuration significantly affects the intensity and uniformity of daylight. This paper aims to investigate the effect of window configuration on daylight performance through parametric analysis. Different window configurations such as window to wall ratio, incorporating light shelves and roof monitors have been analyzed on a typical south-east facing classroom in Kashan based on results from DesignBuilder Radiance simulation which has first been validated against field measurements. Daylighting credits of green building rating tools; Leed EQ 8.1 and BREEAM HEA1 have been used as indices for evaluating and comparing different window configurations. Results show that by increasing the window-wall-ratio to 35, 40 and 50% and by installing a roof monitor, the daylight credits of the BREEAM and LEED could be achieved respectively. According to the fact that none of these window configurations have reached the standards required by both rating tools, the authors believe that a combination of installing monitor roof and light shelves and increasing window-wall-ratio may result in enhanced daylight levels.
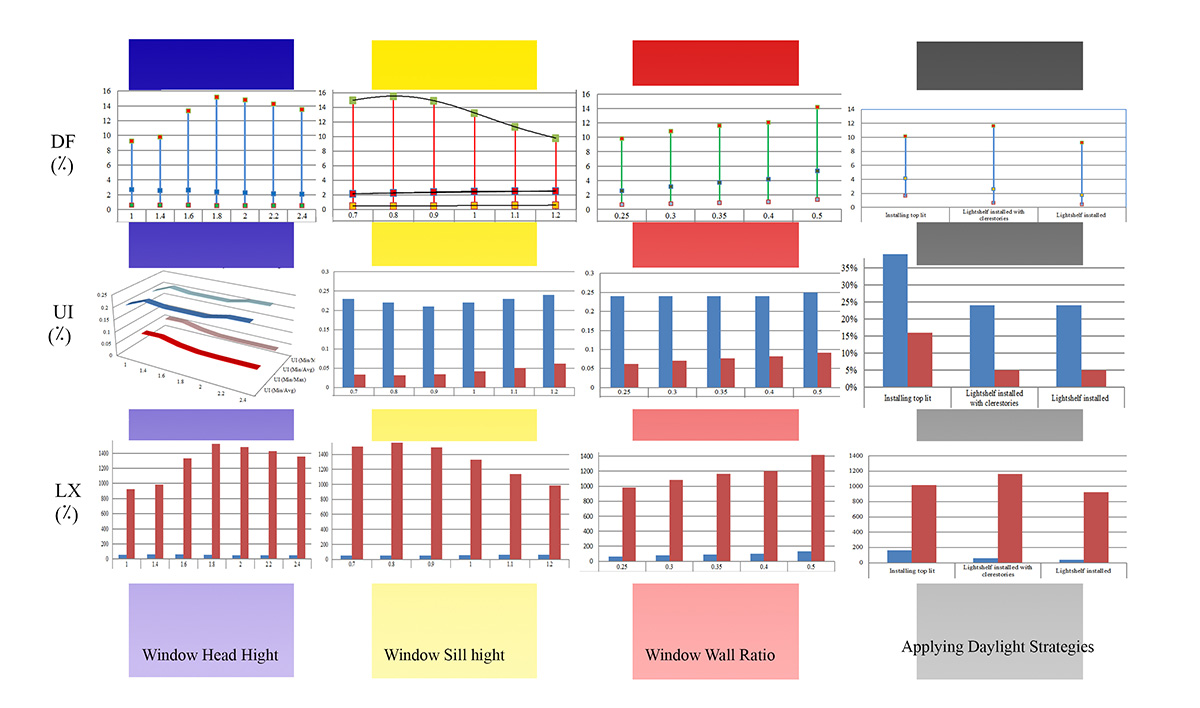
Highlights:
- Window configuration effects on the intensity and uniformity of daylight
- Uniformity increase and glare reduction by light shelves and roof monitors
- Best “daylight performance, better daylight intensity and uniformity via a roof monitor
- Even daylight distribution in sun condition and less overall daylight in overcast, utilizing light shelves
| Rights and permissions | |
 | This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |




