Sat, Nov 30, 2024
[Archive]
Volume 18, Issue 1 (March 2021)
IJMSE 2021, 18(1): 61-70 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Soleimani Gilakjani R, Razavi S H, Seifollahi M. The Effect of Niobium Addition on the Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Iron-Nickel Base A286 Superalloy. IJMSE 2021; 18 (1) :61-70
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1803-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-1803-en.html
Abstract: (11988 Views)
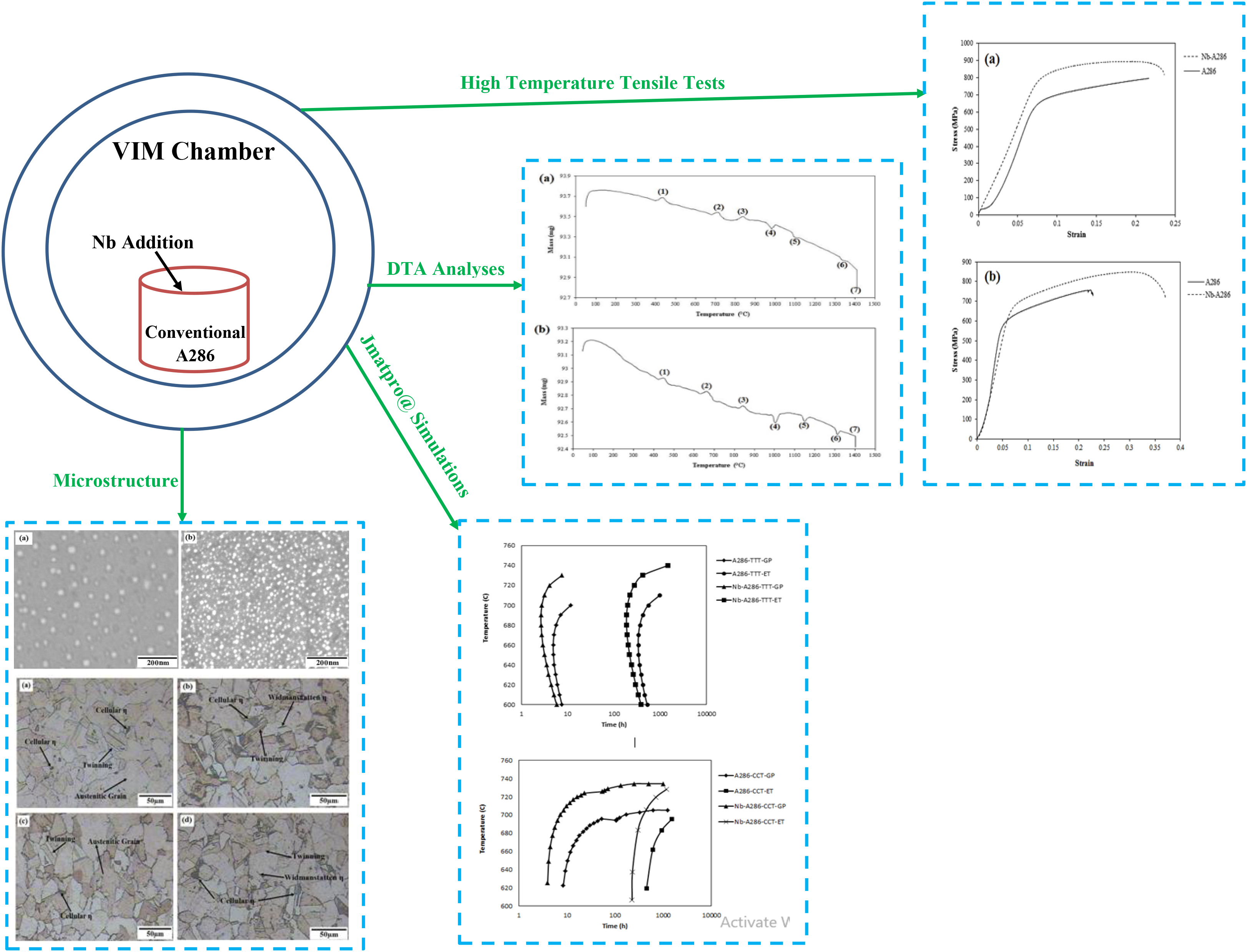
Niobium addition is an appropriate approach for improvement of superalloy’s operation. The purpose of this study is twofold: (1) to investigate on the η and γ/ phase precipitations along with (2) to identify the high-temperature tensile properties in A286 and Nb-A286, as a modified type. The heat treatment of both alloys was carried out in a two-stage aging procedure at 760°C for 16 h and 820°C for 2 to 30 hours, following characterized by optical and Scanning electron (SEM-EDS) microscopies, differential thermal analysis (DTA) and high temperature tensile tests. The results showed that niobium addition was increased the volume fraction of γ/ phase, from 10.7% to 12%, decreased its size, from 94 to 71 nm, and rising the γ/-dissolution temperature from 987°C to 1007°C. Moreover, the γ/ to η phase transformation was sluggishly occurred in Nb-A286 due to more stable of γ/ precipitations. Furthermore, the Nb-A286 alloy demonstrates higher mechanical properties than A286 one, approximately 100MPa improvement, which it was contributed to the much large volume fraction and finer size of more stabilized γ/ phase.
Keywords: A286 superalloy, Niobium addition, η and γ/ phases, microstructure evaluation, hot-tensile properties
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
physical and thermal properties
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |