Wed, Mar 12, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 20, Issue 3 (September 2023)
IJMSE 2023, 20(3): 1-11 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Mahapatra H, Bedia S, Ramasubramanian A, Joshi M, Ghadage M, Bedia A. Upgrading Restorative Dentistry with Graphene Nanoparticles: A Review. IJMSE 2023; 20 (3) :1-11
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3345-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3345-en.html
Hrishikesh Mahapatra 
 , Sumit Bedia
, Sumit Bedia 
 , Aishwarya Ramasubramanian
, Aishwarya Ramasubramanian 
 , Mridula Joshi
, Mridula Joshi 
 , Mahesh Ghadage
, Mahesh Ghadage 
 , Aarti Bedia
, Aarti Bedia 


 , Sumit Bedia
, Sumit Bedia 
 , Aishwarya Ramasubramanian
, Aishwarya Ramasubramanian 
 , Mridula Joshi
, Mridula Joshi 
 , Mahesh Ghadage
, Mahesh Ghadage 
 , Aarti Bedia
, Aarti Bedia 

Abstract: (8340 Views)
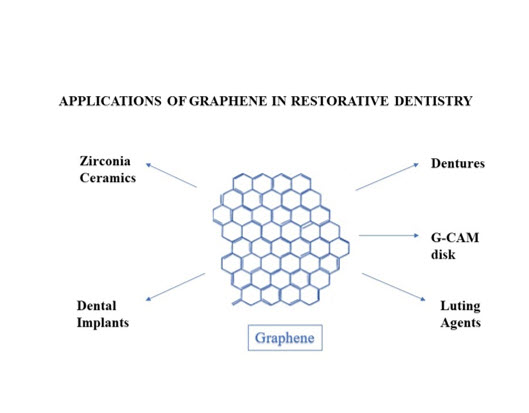
Graphene Nanoparticles (GNPs), an upshot of nanotechnology have attracted great interest in diverse research fields including dentistry for their unique properties. Graphene Nanoparticles are cytocompatible and when combined with other compounds, they possess improved synergistic antimicrobial and anti-adherence properties against oral pathogens. The cytotoxicity of graphene in the oral setting has been reported to be very limited in the scientific literature. Current applications of graphene include reinforcing Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) for the fabrication of dentures, improving properties of dental luting agents like glass ionomer cement, reinforcing restorative composites and ceramics, and improving osseointegration of titanium dental implants by coating with graphene. This paper reviews the nanoparticle ‘Graphene’ and its potential uses in the field of restorative dentistry.
Type of Study: Review Paper |
Subject:
Biomaterials
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |