Thu, Apr 17, 2025
[Archive]
Volume 20, Issue 3 (September 2023)
IJMSE 2023, 20(3): 1-10 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Tanrıverdi A, Tekerek S. The Effect of Boron Reinforced on the Supercapacitor Performance of RGO/ZnO:B Composite Electrodes. IJMSE 2023; 20 (3) :1-10
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3306-en.html
URL: http://ijmse.iust.ac.ir/article-1-3306-en.html
Abstract: (8953 Views)
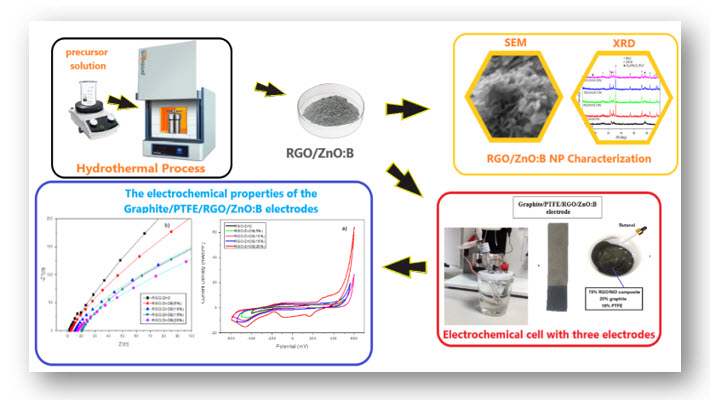
In this study, zinc chloride (ZnCl) was used as a precursor chemical to form boron reinforced zinc oxide (ZnO:B) particles. The supercapacitor performance of the reduced graphene oxide/boron reinforced zinc oxide (RGO/ZnO:B) composite electrodes produced by hydrothermal methods, and the impact of different boron doping ratios on the capacitance, were both examined. The characterization of the RGO/ZnO:B composites containing 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% boron by weight were performed using X-Ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The capacitance measurements of the electrodes produced were conducted in a 6 M KOH aqueous solution with a typical three electrode setup using Iviumstat potentiostat/galvanostatic cyclic voltammetry. The specific capacitance value of the 20% reinforced RGO/ZnO:B composite electrode was 155.88 F/g, while that of the RGO/ZnO composite electrode was 36.37 F/g. According to this result, the capacitance increased four-fold with a 20% boron doping concentration. Moreover, a longer cycle performance was observed for the RGO/ZnO:B electrodes with higher boron doping concentrations.
Type of Study: Research Paper |
Subject:
Composites
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |